News & UpdateS
The network effect
Most recent developments, projects, knowledge, and activities from around the network.
We are Asia’s #1 social investor network
We are a network of 600+ members across 33 markets that is increasing the flow of financial, human, and intellectual capital from around the world into the social sector in Asia. We believe our strength comes from the diversity of our members and partners. They have shown time and again their commitment to connecting across diverse sectors and geographies to move capital towards impact together.
AVPN helps you to move capital towards impact
We are action-oriented. That means we find social investment opportunities in Asia that will drive the global social impact agenda forward and explore how to effectively move capital to where it is needed most.

Deal Share Platform

Philanthropic Funds

Grants From Members


Work together to make significant progress on particular causes that are of common strategic importance.





Gender

Policy Lab
Private Wealth Hub


Explore our library and learn from our research team, our members, and partners through reports, blog posts, events, videos, and tools.
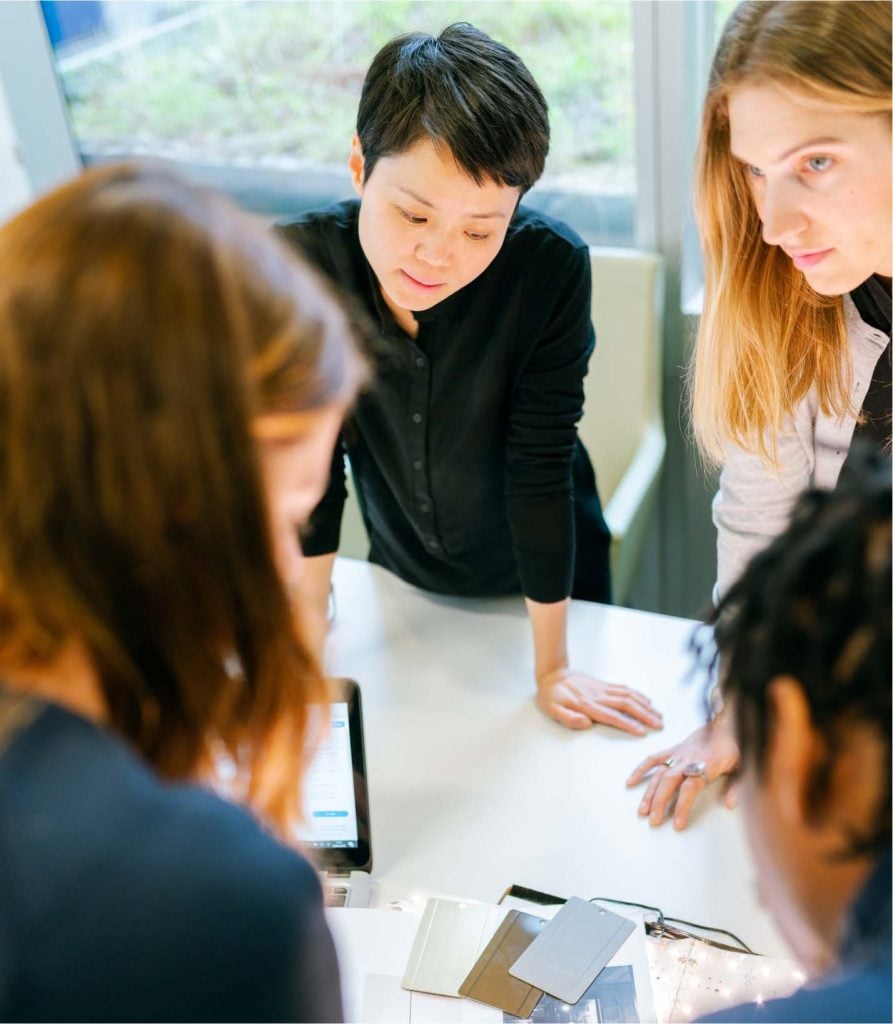





Join a community of peers and learn about new ways of moving capital towards impact through a practitioner lens.






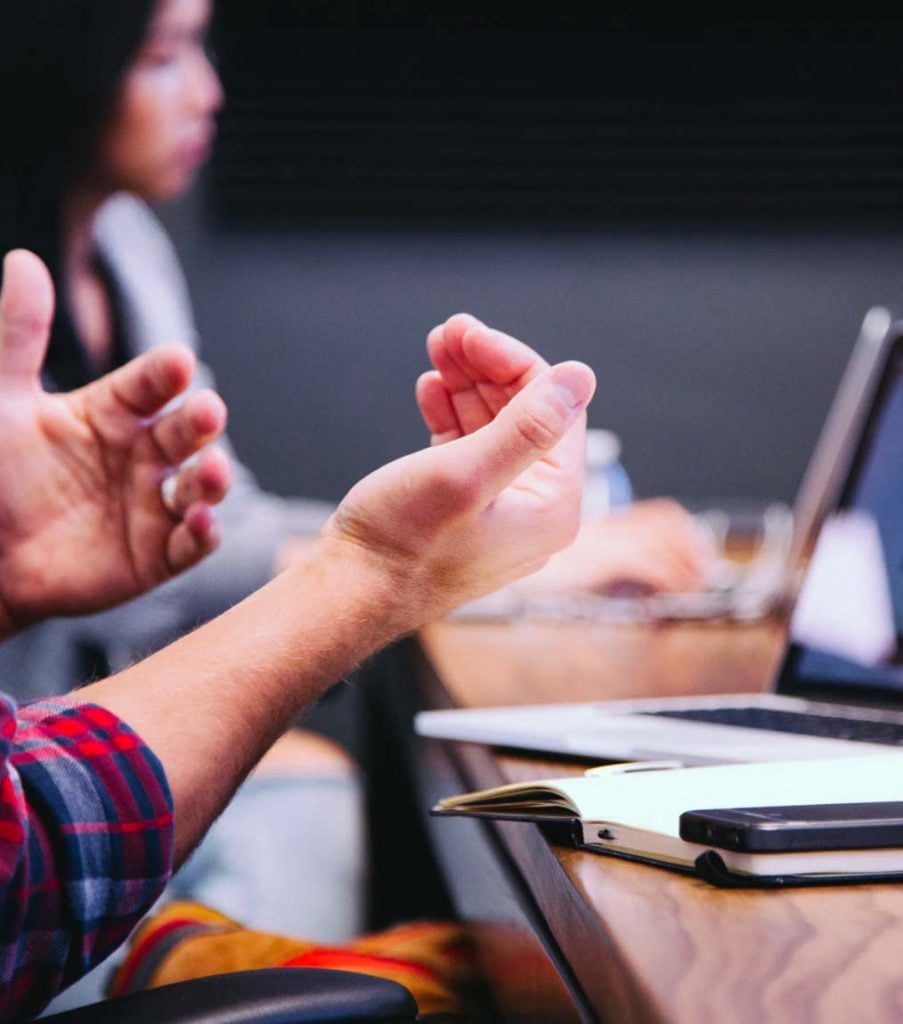
Meet others working to move capital towards impact and learn together.


Explore the social investment landscape across Asia
Click on a market to find out what the AVPN social investor community in that market is doing. About 20% of our members are also headquartered outside Asia, but are active across Asia in collaboration with Asian partners.
Global Market
With 6x the population of any other region, Asia is the perfect place to make an impact and change the world. That's why 20% of our members are from outside Asia and many of our members work across all Asia as Regional and Supporting members. Find out more about them.
Global Market
With 6x the population of any other region, Asia is the perfect place to make an impact and change the world. That's why 20% of our members are from outside Asia and many of our members work across all Asia as Regional and Supporting members. Find out more about them.
Global Market
With 6x the population of any other region, Asia is the perfect place to make an impact and change the world. That's why 20% of our members are from outside Asia and many of our members work across all Asia as Regional and Supporting members. Find out more about them.
Global Market
With 6x the population of any other region, Asia is the perfect place to make an impact and change the world. That's why 20% of our members are from outside Asia and many of our members work across all Asia as Regional and Supporting members. Find out more about them.
Global Market
With 6x the population of any other region, Asia is the perfect place to make an impact and change the world. That's why 20% of our members are from outside Asia and many of our members work across all Asia as Regional and Supporting members. Find out more about them.
Australia
One of the most dynamic economies in the world, Australia has a long-standing giving culture. Local grant-makers are leading the movement towards long-term strategic philanthropy.
Mainland China
A developing market and the 2nd largest economy of the world, China is emphasizing responsible business and investment to build a society of mutual prosperity.
Japan
An upper-middle-income country driven by religious values, Japan is fast becoming a hub for responsible investment. Its drive for innovation continues to underpin its emerging social investment market.
South Korea
After several decades of demonstrating rapid economic growth, South Korea is now sprouting demand for sustainable investing. With the new goal of increasing up to 50 percent of its investment in ESG assets by 2022, the country aims to set an example of social responsibility in Asia.
Indonesia
Indonesia remains poised to become the 4th largest economy in the world by 2030. Impressive growth in recent years along with the country's rich tradition of giving and the enhancement of SDGs implementation provide a strong foundation for the social investment ecosystem.
Malaysia
Malaysia's drive for innovation continues to underpin its emerging social investment market. The government is making a concerted effort to grow and support the impact ecosystem.
Singapore
Singapore has a very robust and vibrant social investment ecosystem. Singapore is the gateway to the rest of Asia with several international relationships flowing through the Southeast Asia Hub. Singapore is well positioned to lead social investment in the region.
Philippines
With GDP growth rates hovering around 6.9%-7%, the Philippines is one of the top performers in Asia. While the pandemic has slowed growth, the country is positioned for a solid recovery. Strong civil society sector and the presence of many international social investors are catalysts for the country to achieve recovery and sustainable development.
Myanmar
The amazing story of Myanmar is that despite great political turmoil (a nascent but unstable democracy) their economy is among the fastest growing in the world. It is no wonder Myanmar is attracting a lot of investment in stable times. An emerging market country driven by a hunger for innovation and growth, Myanmar is a key country to watch for progress in affordable sustainable investment. Social impact investors however need to play a role to help stabilize democracy in such strife-torn countries.
Cambodia
One of the fastest growing emerging economies in the world, Cambodia has been ranked as one of the least developed countries, so has a strong investment landscape potential. With a strong social sector and government support Cambodia has become a world leader in reducing poverty. Political stability gains have meant investment in Cambodia is ready to be unleashed. However, the strength of labour is weak, and so much potential for Cambodia is still dormant, worker rights have much room for improvement and domestic demand has significant under-utilized capacity.
Thailand
A middle-income country with strong collective values and proud history of independence, Thailand is an emerging economy, heavily export-dependent, with exports accounting for more than two-thirds of gross domestic product (GDP). Thailand is a pivotal market in SEA owing to the concentration of multinationals in Bangkok. It is a hub for investment companies and NGO's in SEA. Famous for tourism and hospitality, Thailand has difficulties ahead for sustainable tourism and reducing harm to the environment and could sustain more healthy domestic tourism.
South Asia
An upper-middle-income country driven by religious values, South Asia is fast becoming a hub for responsible investment. Its drive for innovation continues to underpin its emerging social investment market.
Vietnam
An upper-middle-income country driven by strong economic development, Vietnam is also fast becoming a hub for responsible investment. Its drive for innovation continues to underpin its emerging social investment market.
Hong Kong SAR China
One of the most dynamic economies in the world, Hong Kong SAR China is a significant gateway for international capital and has a long-standing giving culture. Local mega grant-makers are leading the movement towards long-term strategic philanthropy.
With 6x the population of any other region, Asia is the perfect place to make an impact and change the world. That’s why 20% of our members are from outside Asia and many of our members work across all Asia as Regional and Supporting members. Find out more about them.
One of the most dynamic economies in the world, Australia has a long-standing giving culture. Local grant-makers are leading the movement towards long-term strategic philanthropy.
A developing market and the 2nd largest economy of the world, China is emphasizing responsible business and investment to build a society of mutual prosperity.
One of the most dynamic economies in the world, Hong Kong SAR China is a significant gateway for international capital and has a long-standing giving culture. Local mega grant-makers are leading the movement towards long-term strategic philanthropy.
An upper-middle-income country driven by religious values, South Asia is fast becoming a hub for responsible investment. Its drive for innovation continues to underpin its emerging social investment market.
An upper-middle-income country driven by religious values, Japan is fast becoming a hub for responsible investment. Its drive for innovation continues to underpin its emerging social investment market.
After several decades of demonstrating rapid economic growth, South Korea is now sprouting demand for sustainable investing. With the new goal of increasing up to 50 percent of its investment in ESG assets by 2022, the country aims to set an example of social responsibility in Asia.
Singapore has a very robust and vibrant social investment ecosystem. Singapore is the gateway to the rest of Asia with several international relationships flowing through the Southeast Asia Hub. Singapore is well positioned to lead social investment in the region.
Malaysia’s drive for innovation continues to underpin its emerging social investment market. The government is making a concerted effort to grow and support the impact ecosystem.
Indonesia remains poised to become the 4th largest economy in the world by 2030. Impressive growth in recent years along with the country’s rich tradition of giving and the enhancement of SDGs implementation provide a strong foundation for the social investment ecosystem.
With GDP growth rates hovering around 6.9%-7%, the Philippines is one of the top performers in Asia. While the pandemic has slowed growth, the country is positioned for a solid recovery. Strong civil society sector and the presence of many international social investors are catalysts for the country to achieve recovery and sustainable development.
The amazing story of Myanmar is that despite great political turmoil (a nascent but unstable democracy) their economy is among the fastest growing in the world. It is no wonder Myanmar is attracting a lot of investment in stable times. An emerging market country driven by a hunger for innovation and growth, Myanmar is a key country to watch for progress in affordable sustainable investment. Social impact investors however need to play a role to help stabilize democracy in such strife-torn countries.
One of the fastest growing emerging economies in the world, Cambodia has been ranked as one of the least developed countries, so has a strong investment landscape potential. With a strong social sector and government support Cambodia has become a world leader in reducing poverty. Political stability gains have meant investment in Cambodia is ready to be unleashed. However, the strength of labour is weak, and so much potential for Cambodia is still dormant, worker rights have much room for improvement and domestic demand has significant under-utilized capacity.
A middle-income country with strong collective values and proud history of independence, Thailand is an emerging economy, heavily export-dependent, with exports accounting for more than two-thirds of gross domestic product (GDP). Thailand is a pivotal market in SEA owing to the concentration of multinationals in Bangkok. It is a hub for investment companies and NGO’s in SEA. Famous for tourism and hospitality, Thailand has difficulties ahead for sustainable tourism and reducing harm to the environment and could sustain more healthy domestic tourism.
An upper-middle-income country driven by strong economic development, Vietnam is also fast becoming a hub for responsible investment. Its drive for innovation continues to underpin its emerging social investment market.
Explore the social investment landscape across Asia
Click on a market to find out what the AVPN social investor community in that market is doing. About 20% of our members are also headquartered outside Asia, but are active across Asia in collaboration with Asian partners.
Our Markets
Explore the social investment landscape across Asia
Click on a market to understand more about its social investment landscape and the market opportunities to drive impact.
Impact Communities
Connect to unusual allies with common goals
MEMBERS' WORK
Humanitarian relief efforts
Opportunities to support the ongoing humanitarian work of our members across the region.
If we cannot be at the vanguard, we must stand at the backs of those who are there with practical solidarity.
What do our members think about AVPN?

Chief Functionary, Azad Foundation


Director of International Programs, Nomi Network

Executive Director, Badabon Sangho
Need help getting started?
Here are some directions and links that may help you fulfil your goal today.

Are you currently doing research on the impact space? Uncover the latest insights and perspectives from investors, practitioners, and sector leaders.

Are you looking to join conversations and be plugged into the network to grow your knowledge? Check out our upcoming events!

Are you from an Impact Organisation? Visit Deal Share Platform and list your project!








































